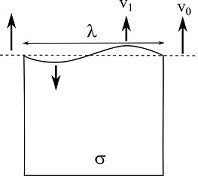
Crack front instabilityWe have shown that some crack fronts become unstable at low velocity : they start to undulate (instead of propagating straight) and two coupled fronts bifurcate (one stops while the other one keeps propagating). We have observed this behaviour in laminated glass but also found other examples in the literature. Through numerical simulations, we have shown that this instability is actually due to emerging viscoplasticity at low velocity. For more detail see this paper. |
 |
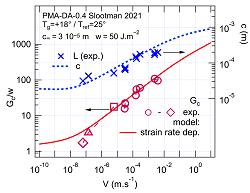 |
The linear viscoelastic fracture theory applies to soft solids better when they are…viscoelasticIn the field of soft matter fracture, new in situ techniques reveal the size of the zone where material damage occurs, around the crack tip. I took this opportunity to revisit the conditions of applicability of the "stabdard model" of soft matter fracture, the linear viscoelastic crack model. For more, see this paper. |
Dynamic ruptureLaminated glass is a sandwich of a thin PVB polymer film inside two glass plates. Paul Elzière investigates how PVB adheres and how laminated glass breaks. |
 Impact on flat laminated glass Impact on flat laminated glass |


